What are futures?
Futures are standardized contracts which, like options, are made between two parties at a fixed price and expiry date. It is a contract to deliver an underlying product at an agreed time in the future at an agreed price, hence the name. They are a type derivative because the underlying product itself is not owned. Rather, it obtains its value from the price of an underlying asset. This can be an index, a financial instrument or a commodity.
How do futures work?
A futures contract is a negotiable contract that relates to the purchase (long) or sale (short) of an underlying asset. Delivery will take place in the future at an agreed-upon date and price. Buyers and sellers have opposing expectations of how the underlying’s value will materialise. A buyer will realise a gross profit when there is an increase in the value of the underlying at the closure and will realise a gross loss when the value of the underlying has decreased. Moreover, if you take a long position when trading futures contracts, you think that the underlying price will increase. Like many other derivatives, they have a contract size where each future has a fixed number of the underlying product as the underlying value.
How are futures settled?
The payment for a futures contract is made at the end of the agreed term. This can be done by physical delivery or a cash settlement. Index futures, such as FTSE futures, are usually settled in cash. With physical delivery, the specified goods are actually delivered. This, however, does not happen often since they are regularly sold before they expire. One of the top reasons for investing in this type of financial product is to make a profit by taking advantage of price differences in the underlying securities. Therefore, cash settlement is more common than physical delivery. There is no flow of money with buying and selling. The agreed price must only be paid upon delivery. However, a broker will require a down payment because of the large commitment that has been made.
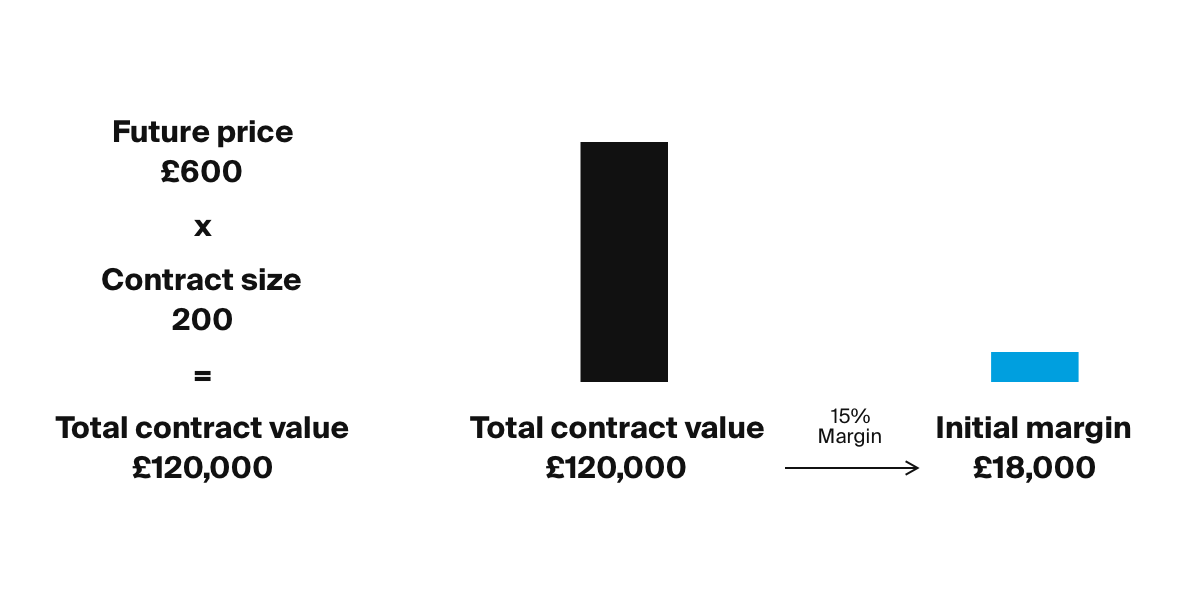
Say you think a stock index will go up. It is at 600 points, and you consider a futures contract with a contract size of 200. The value of this futures contract would be €120,000. When trading futures, you do not pay this whole amount at the time of purchase, but typically put down an initial margin to enter into the contract. Say there is a margin rate of 15%. You would get a €120,000 exposure to the underlying by making a deposit of at least €18,000 as margin to your account. This means you can get a large exposure for a small initial margin with a futures contract. If the index would go down and your margin becomes less than 15%, you will receive a margin call, asking you to increase it above the 15% threshold.
Unlike options, futures are settled on a daily basis. This means that if the future has gained 3 points at the end of the trading day, you will receive 3 times the €200 multiplier, for an amount of €600. Do note that because the contract size is bigger than the margin, it is also possible to lose more than your deposit with futures.
Futures and hedging
Futures are a common derivative used to hedge risk. Companies and investors use them to neutralise risk as much as possible. This is done by removing the uncertainty of a future price of an item or financial product. You are able to use short and long hedges. With a short hedge, one enters into a short position on the contract. They are typically initiated by traders who own an asset and are worried about prices declining before the sales fate. On the other hand, a long hedge occurs when one enters into a long position. For example, if a company knows it needs to purchase a particular item on a future date, and the current spot price is higher than the future price, they can lock in the lower price. This removes the uncertainty off the future price of a product.
Costs and margin involved with trading in futures
ESKIMO charges connection fees, transaction costs and settlement costs for trading along with investment cost. You can find these costs in the cost overview. You only pay settlement costs at the final settlement upon expiration, not before.
As previously stated, a broker requires collateral for the commitment that has been made. This reserved amount is called the initial margin. Given the high risk, this can be a considerably high amount. ESKIMO created a risk model, which is used to determine the amount of collateral required. In case the price of the underlying asset differs from what you have expected, you can often meet your obligation with this reserved amount.
How can you invest in futures with ESKIMO?
At ESKIMO, you can trade in futures on a number of affiliated derivatives exchanges. Due to their relatively high risk and their complexity, they are not suitable for inexperienced investors. Therefore, with a ESKIMO account, you cannot directly trade in derivatives. You will need an Active or Trader account, which comes with additional appropriateness tests and terms and conditions.
Trading in derivatives, such as futures, can be very profitable, but it comes with substantial risk. On the upside, you can profit from the leverage effect, which allows you to achieve a high return on your investment. On the downside, however, you can lose more money than your initial stake. Futures are complex financial products. At ESKIMO, we are open and transparent about the risks that are related to investing. You do not have to pay for anything when opening a future position. But you do enter into an obligation with a futures contract. ESKIMO does not facilitate the settlement of physically delivered contracts. We inform customers about an upcoming expiry and request the position to be closed on time. If that does not happen, ESKIMO closes the position for the investor to prevent, for example, having to buy a number of barrels of oil. We, therefore, ask for collateral. In some exceptional situations, the losses an investor experiences can be higher than this collateral. If you have insufficient collateral according to our risk model, we can ask you to make a deposit or to lower your risk. If you do not solve the deficit in time or if your risk becomes too high according to the model, ESKIMO can intervene. It is recommended to only enter into obligations that you can meet with money that you do not need in the short term.
The information in this article is not written for advisory purposes, nor does it intend to recommend any investments. Please be aware that facts may have changed since the article was originally written. Investing involves risks. You can lose (a part of) your deposit. We advise you to only invest in financial products that match your knowledge and experience.
Start investing today.
Start investing today.
- Fast & Easy.
- Comprehensive tools, capabilities, and service.
- Worldwide. Anytime and anywhere.
- Secure structure.